Blog Posts
Top Reasons Why Research Papers Get Rejected
eR Blog
Business
Business writing has to be clear, precise and easy to read. The style needs to be professional and courteous but not overly formal. There should not be too many extra words, like adjectives and adverbs, nor there should be any clichés.
The purpose of business writing is to get work done—to recommend actions. It is written to solve problems, store vital information, negotiate new contracts, map out future direction of the company or institution, track quality control benchmarks, report earnings etc.
Business writing is all about relationship building and selling, not only about products and services but about ideas, courses of actions, recommendations and personal and company image. Therefore an effective business writer must be able to use three tones: formal (reports), neutral (letters) and informal (emails).
Academic
Academic writing presents arguments without loaded or biased language. The author is expected to investigate the research problem from an authoritative point of view. The strengths of the arguments are stated in a neutral, not confrontational or dismissive manner.
The writing produced in academic settings can best be described as "writing to learn" and "writing to demonstrate" what you learned. Its purpose is more to inform and educate rather than to persuade.
Generally, academic writing is expected to be precise, semi-formal, impersonal, objective, analytical and critical. Arguments are informed—clear, concise and persuasive. Opinions and judgments are based on facts.
Aspect
Language & Style
Purpose
Tone
What problems do ESL writers have with writing papers in English?
The challenges faced by ESL (English as a Second Language) writers when writing research papers in English are high, notes Yeen Lau (2014), Product Manager at BioMed Central. She believes that this is because authors have to conduct research in one language (their first language) and write in a language which is not their own. This is especially true when using sources. Finding ones own individual voice among other writers' voices is problematic.
To be specific, ESL writers find it difficult when choosing words or phrases that are suitable for the content. Besides, faulty construction of sentences, unidiomatic expressions, and odd usage deflects a reviewer’s attention from the substance of the paper to its style (Yateendra Joshi, 2014) and makes sentences often sound awkward. To some extent, the awkwardness can be contributed to differences in syntax between writers’ native language and English. Syntax refers to the rules of grammar⎯rules for ordering and connecting words in a sentence. Besides, in an effort to get the point across, ESL writers tend to repeat themselves, saying the same thing more than once. The problem is not just saying the same thing, but also repeating the same sentence structure, particularly verbs. This results in superfluous information, making the writing too verbose, not to mention dull and tedious for the reader. Yeen Lau says “rather than counting every word, it is more important to make every word count”.
1. Yeen Lau. 2014. The challenges of getting your research published when English is not your first language. BioMed Central blog.
Yeen Lau. 2014. The challenges of getting your research published when English is not your first language. BioMed Central blog.
2. Yateendra Joshi. 2014. Can poor English affect the publication and impact of research? English Communication, Editage Insights.
Yateendra Joshi. 2014. Can poor English affect the publication and impact of research? English Communication, Editage Insights.
Why is it important to proofread and edit?
Simple errors can lead to disappointment and failure
People judge you based on your overall appearance. When you need to impress a client, a colleague, your boss or your professor, then don’t leave anything to chance.
Your content demonstrates your professionalism.
You don't want to jeopardize the chances of your PhD approval, paper acceptance, client's full satisfaction, or business profitability, just because you failed to pay attention to the details.
Your content presentation speaks about your enthusiasm and determination.
A neatly written article without any errors and with a crisp content, creates a good impact on your prospects and clients. It sends out a powerful message that you are articulate and comprehensive with the presentation of your subject matter, research work, services or products.
Your content quality is a representation of your knowledge.
A well-written paper clearly suggests that as an academic, a business owner or manager, you are knowledgeable and take your work seriously.
Proofreading Is Not Just Spell Check. It is the decisive factor between a poorly presented and an effective and error-free document.
essayRight Proofreading & Editing Services
Your success is
our success
CUSTOMER SERVICE
essayRight Proofreading and Editing Services
Authors invariably are blind to their own work. So they need an extra pair of eyes. At essayRight, every submission goes through two professional editors.
TWO PAIRS OF EXTRA EYES
Is good English an important factor in publishing academic papers?
English has become the language of choice in many countries where great emphasis is placed on publishing in national and international journals(1). With increasing globalization, this trend is on the rise. Little wonder that most academics and scholars striving for international recognition today aspire to publish their articles in English(2). However, for many of them, poor English is one factor that puts them at a disadvantage(3).
“Clarity in writing reflects on clarity in thought”(4). Further, first impressions are always crucial. Readers can only grasp the full message or impact of your work when the language is clear and proper. From this perspective, too often, the issue of first language—whether it is English or otherwise—turns out to be of practical relevance. Therefore, it is imperative that authors make sure that their manuscripts go through professional editing before submission. Otherwise, authors should be prepared to face delays in the publication (or even outright rejection) of their papers. Remember that top journals reject many of the papers submitted to them before they even reach the peer-review stage.
1. Research Trends. July 2008, Issue 6.
2. Bilal Glenc and Erdogan Bada. 2010. English as a World Language in Academic Writing. The Reading Matrix, 10(2).
3. News Scientist. 2004.
4. Stephen, M. Griffies, William A. Perrie and Gaelle Hull. 2013. Elements of Style for Writing Scientific Journal Articles. Elsevier. P. 3.
B) Accepted, under the condition that major revisions are made.
The study adds value to the field, but needs major rewriting due to weaknesses in terms of the following:
1. Problems with methodology, presentation of results and discussion.
Problems with methodology, presentation of results and discussion.
- The study lacks clear control groups or other comparison metrics.
- The analysis is not statistically valid.
- The arguments are illogical, unstructured or invalid.
2. The conclusions cannot be justified on the basis of the rest of the paper.
- The data does not support the conclusions.
3. References are incomplete.
- There is a mismatch between the in-text citations and items in the reference list. Those cited in the manuscript are not included in the reference list or vice versa.
- Referencing format is inconsistent.
- The reference list items are very old.
4. The writing sounds inexperienced.
- The paper is front loaded with too much literature and lacks a strong conclusion that deals with the “So What?” and “Now What?” questions.
- There is too much time spent on method, or the paper is weighted too heavily on results, or there isn’t enough grounding for the study, or enough analysis.
5. There are grammar errors that need to be fixed. Recommend professional editing service.
Source: https://www.elsevier.com/connect/8-reasons-i-rejected-your-article
https://www.elsevier.com/authors-update/story/peer-review/how-reviewers-look-at-your-paper-your-questions-answered
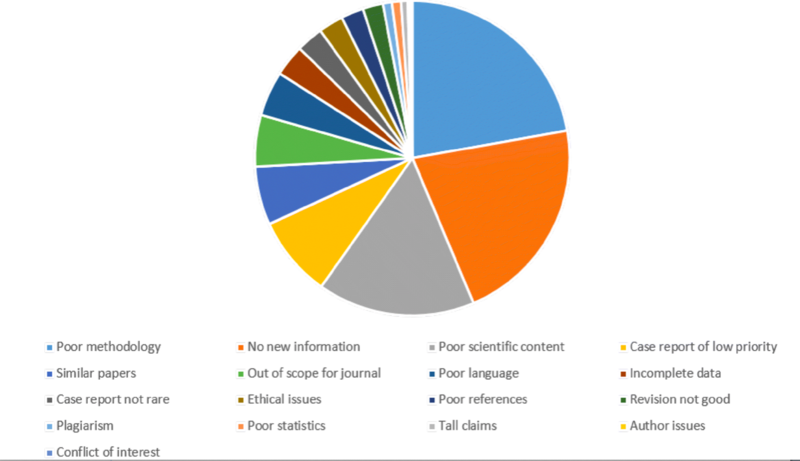
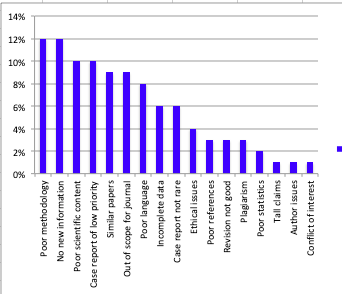
Top Reasons Why Research Papers Get Rejected
Source: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13224-018-1153-1
Rejection Blues: Why do Research Papers Get Rejected
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India
Details about why journal editors/reviewers reject your paper:
A) Outright rejection
1. It fails technical screening.
It fails technical screening.
- The article contains elements that are suspected to be plagiarized.
2. The paper is incomplete.
The paper is incomplete.
- The article contains observations but is not a full study.
3. The writing is incomprehensible.
The writing is incomprehensible.
- The language and essay structure are so poor that merit cannot be assessed.
4. The article does not conform to the Author guidelines for the journal it is submitted to.
The article does not conform to the Author guidelines for the journal it is submitted to.
5. The paper is not of value to the field.
The paper is not of value to the field.
- The authors are reporting a piece of research without any convincing information to show that it is important.
6. The findings are incremental, they do not add new information to the field.
The findings are incremental, they do not add new information to the field.
7. The paper is overcrowded with ideas. It lacks focus.
The paper is overcrowded with ideas. It lacks focus.
8. The procedures and/or the analysis of the data is seen to be defective. The research is too basic, with a weak hypothesis.
Reasons for rejection